The openZDM Platform in a world driven by the 4th Industrial Revolution

In the second instalment of the exlusive insights and expert opinions from the openZDM project partners series, we are delighted to showcase the Netcompany-Intrasoft, which also serves as openZDM’s key industrial partner for architecture development, framework and openZDM design and infrastructure.
In the context of the fourth Industrial Revolution the openZDM Platform promotes zero defects in manufacturing through various tools like the Digital Twin, Data Analytics for quality prediction and Non-Destructive Inspection (NDI) tools. The openZDM platform will be built upon innovative technologies like the type 3 Asset Administration Shell, pushing towards green and sustainable manufacturing. Furthermore, it will enable data sharing across
companies through the incorporation of the International Data Space technologies.
The openZDM Platform
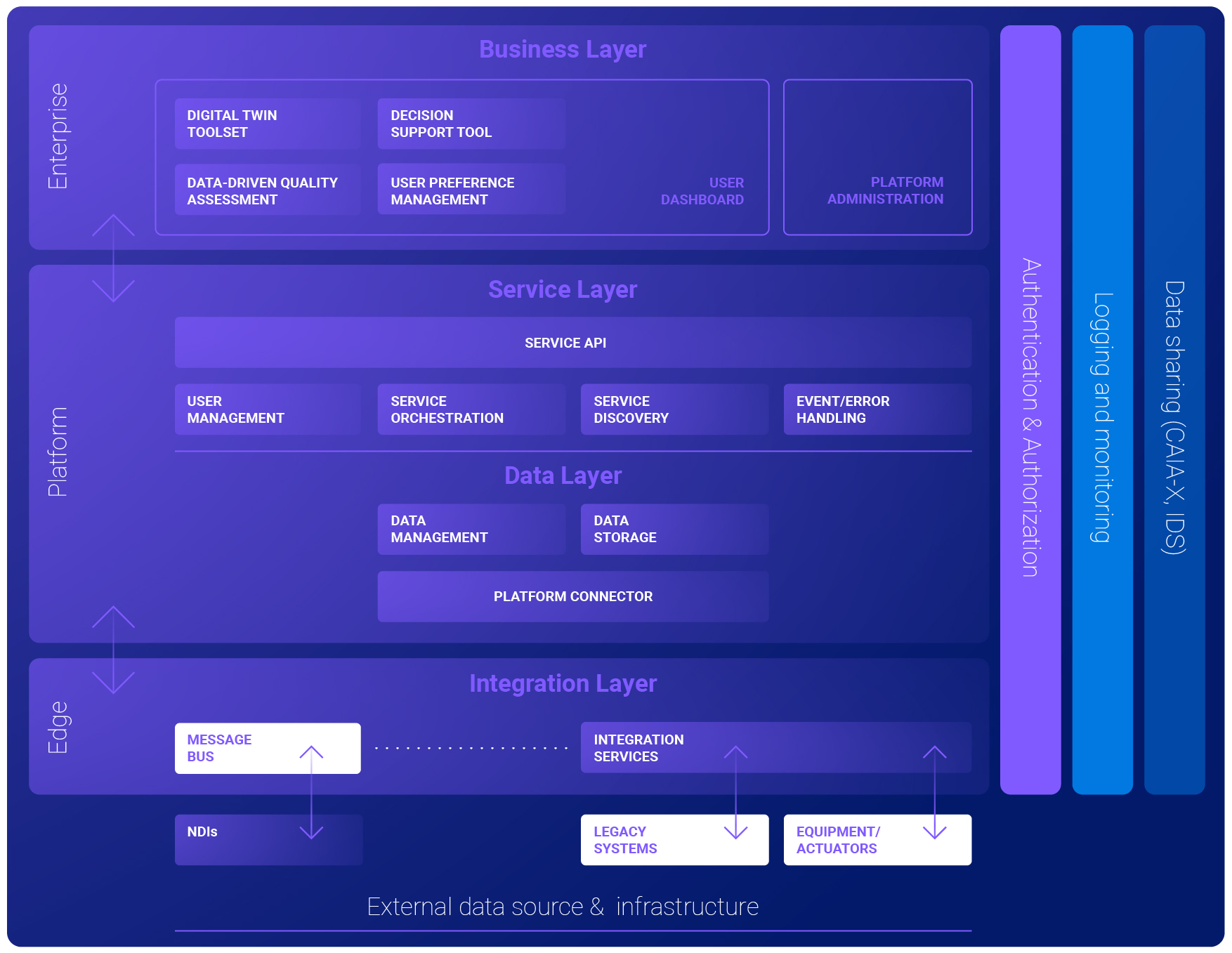
The OpenZDM platform architecture is the result of a thorough analysis of the requirements of the five end users who participate in the project. It enables the interoperability with digital manufacturing ecosystems, legacy and state of the art systems, proprietary and open source technologies through various connectors.
The openZDM Platform Architecture
The architecture of the openZDM platform is comprised of layers and tiers, following RAMI4.0. Each tier can be either deployed on the cloud, locally deployed or hybrid. Each layer of the platform is responsible for grouping together specific components and facilitating specific requirements. The platform layers include the following horizonal layers:
- External data source and infrastructural layer: This layer represents all the assets of the end-users that need to be connected to the openZDM platform.
- Integration layer: The integration layer facilitates the communication between the platform and all the assets.
- Data layer: The data layer’s role is to intercept messages from all the assets.
- Service layer: In the service layer, components that implement some of the platform’s functionalities are included and the layer facilitates access to the data layer form applications in the Business layer (Service API).
- Business layer: This layer groups together the functionality that is offered to the users.
The architecture also includes the following vertical layers, which provide functionalities to all the horizontal layers and the entire openZDM platform architecture is represented in the picture below.
- Authentication & authorization: Provides functionalities for user and services identification, mechanisms to secure communications and authorization mechanisms that permit access to resources of the platform.
- Logging & Monitoring: This layer logs user activity and records system errors.
- Data sharing: The data sharing layer enables the integration of the platform to a data sharing ecosystem.
The Innovation Potential of the openZDM Platform
One of the main innovations which will be implemented in the openZDM platform is the Asset Administration Shell (AAS) and more specifically the type 3 AAS, supporting the interaction and communication of AASs. This is expected to allow for interoperability in smart factories, something reinforced by the open nature of the platform. In the context of Industry4.0 (I4.0), an I4.0 component consists of an asset and administration shell which represents an asset in the digital world, as described in IEC63278-1. In the openZDM platform, after following the type 3 AAS definition, assets can have an active
behavior and communicate or negotiate on their own and their interactions follow a procedure based on the following dimensions:
- Information flow: Unidirectional versus bidirectional in the manifestation.
- Information processing: Three subdimensions which include state, determinism, and synchronicity with the relevant manifestations stateful versus stateless, deterministic versus non-deterministic and synchronous versus asynchronous.
Benefits for Manufacturers
The openZDM platform pushes the industry towards green manufacturing. Green manufacturing and sustainability are essential for a modern manufacturing company. Through the openZDM platform the following aspects of sustainability can be achieved:
- Environmental sustainability: By using technologies like NDIs, Data Analytics and Digital Twins, manufacturers can prevent defects or change their control parameters to achieve higher production yield rates.
- Economic sustainability: The environmental sustainability aspect which a manufacturer achieves through the openZDM platform translates to economic sustainability too, due to the fact that a lower number of defects and higher production yield rates always equals to lower costs and higher profit margins for the company.