The Role of Data Analytics Tools in zero defects manufacturing

In our eight instalment of the exclusive insights and expert opinions from the openZDM project partners, we are hosting researchers from CEDRI -Research Centre in Digitalization and Intelligent Robotics from Instituto Politécnico de Bragança.
Data Analytics Tools (DATs)
The “data-driven” term is related to decision-making based on data analyses, which involves moving from a subjective interpretation to a more objective one based on the available data. This essentially means that the collected data can be analysed and interpreted, generating insights that can be used to drive actions.
In this sense, Data Analytics tools (DATs) encompass various data analysis techniques, e.g., statistical or Machine Learning algorithms, that can be applied in different industrial data analysis contexts to improve production processes in terms of efficiency, productivity, cost reduction, product quality improvement, and market competitive advantage.
Benefits and contributions of DATs in the Zero-Defect Manufacturing (ZDM) context
In the ZDM context, DATs can be used to provide a set of tools for monitoring and analysing the collected shop floor data. Through these tools, some algorithms, methods, or techniques can be implemented to enable anomaly detection, statistical analysis, data prediction, pattern recognition, data correlation, and many other features.
The correct analysis of the gathered data brings a series of benefits that can be highlighted, such as the early detection of defects and problems, reduction of waste and rework, adaptability and reconfigurability in response to changing conditions, enhancement of the process efficiency and optimization, reduction of the cost related to downtime and maintenance, and mainly to the overall improvement of process and product quality.
Catalogue of DATs in openZDM
In the openZDM project, a catalogue of DATs is being developed for monitoring and analyzing shop floor data in multi-stage production, also guaranteeing the semantic interoperability of the tools not only for its validation on the different uses cases, but also easily enabling its deployment to different data inputs on the platform.
The DATs developed in openZDM can be split into four different clusters: pre-processing for data cleaning and synthetic data generation, monitoring for real-time visualization and detections of anomalies and defects, prediction and classification for the early detection of defects and for quality assessment, and descriptive and prescriptive for decision support through explanations of defects causes and actions recommendations.
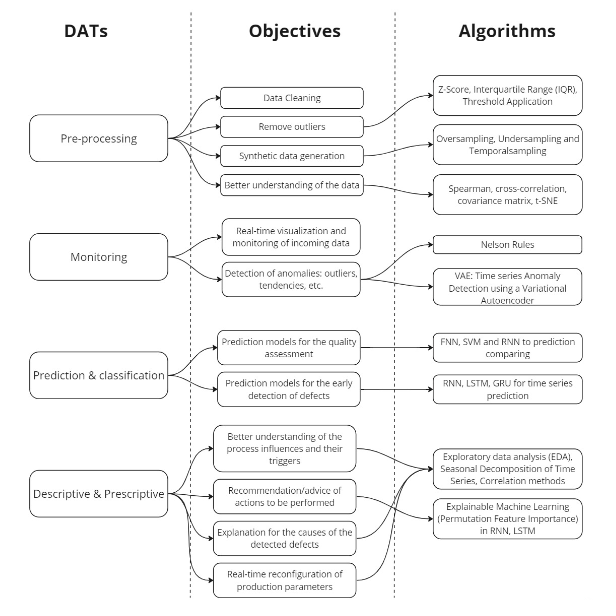
Associated to each referred cluster, several algorithms and techniques are considered and implemented. As example, in the cluster “Monitoring”, the Monitoring Dashboard, Nelson rules, and Variational Autoencoder techniques are considered.


