The role of Asset Administration Shell standard in zero defects manufacturing

In our seventh instalment of the exclusive insights and expert opinions from the openZDM project partners, we had a pleasure to talk with Johnny Alvarado Domínguez, Senior Researcher at AIMEN Centro Tecnológico.
The role of the Asset Administration Shell
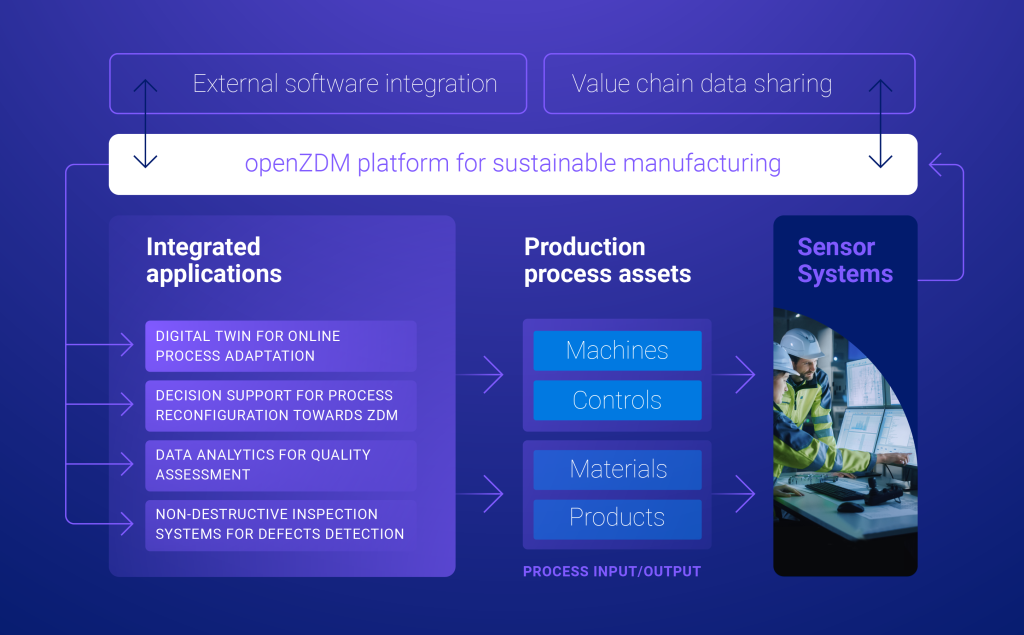
Zero Defect Manufacturing (ZDM) incorporates tools such as Non-destructive Inspection Systems (NDIs) and Industry 4.0 technologies, such as the Internet of Things, Machine learning, and artificial intelligence, among others, in the manufacturing process to achieve the reduction of defective products, rework, and waste. A NDI is a tool used to inspect every quality characteristic in all items from the earliest stages of the production process, to avoid processing materials that do not comply with quality specifications.
In openZDM, NDIs are based on innovative technologies such as X-ray, vision systems, laser line triangulation, X-ray diffraction analysis, machine learning, and Artificial Intelligence. Real-time data capture, monitoring, and analysis are fundamental requirements for zero-defect manufacturing. However, since the resources available in the plant are manufactured by different vendors, which use different data formats, the data generated in the production
process are heterogeneous, making the interoperability between the resources on the shop floor more difficult.
The Asset Administration Shell (AAS) allows interoperability between the shop floor resources providing standardized information.
About Asset Administration Shell
An AAS allows the description of production plant resources, exposing information about their different characteristics and their capabilities in a machine-readable format, which ensures interoperability between these resources (robots, software, processes). The information related to an asset is described by means of submodels. There are no mandatory submodels,
however, they must be able to capture the information required for each use case for which the AAS is designed. A digital twin that mimics the behavior of a physical asset can be implemented by means of an AAS.
In OpenZDM AAS will be created for NDIs, products, and processes to implement digital twins to simulate, monitor, and forecast their behavior.
Using AAS, it is possible to capture information from the manufacturing process of a product in real time, including from legacy systems. This makes it possible to develop tools that support decision-making not only in terms of quality but also in terms of cost and sustainability.
openZDM will be validated and demonstrated in 5 use cases (pilots) in the metalworking, automotive and manufacturing sectors – and will be available for testing on demonstration lines at VDL Weweler, Volkswagen Autoeuropa, VIDRALA, SONAE, SONAE Arauco PT, SONAE Arauco ES and APTIV facilities.
Summary
The AAS is a tool that allows information from the production plant to be captured in a standard format so that later data-driven tools can be developed to support decision-making. These tools will enable zero-defect manufacturing and contribute to cost reduction and sustainability.